Renewable Energy Projects in India: A Stable Energy Future
India, with its burgeoning population and rapidly growing economy, has an increasing demand for energy. To meet this demand sustainably, India is turning to renewable energy sources. While solar and wind energy have seen significant growth individually, hybrid renewable energy projects, which combine these two sources, are emerging as a promising solution for a more stable and reliable energy supply.
These systems combine two or more renewable energy sources, often wind and solar, to generate electricity. This combination allows for a more consistent energy supply, as the intermittency of one source can be offset by the other. For example, solar power generation peaks during the day, while wind power is often stronger at night and during the monsoon season when there is less sunshine. By combining these two, a more continuous and stable power output is achieved throughout the day and across seasons.
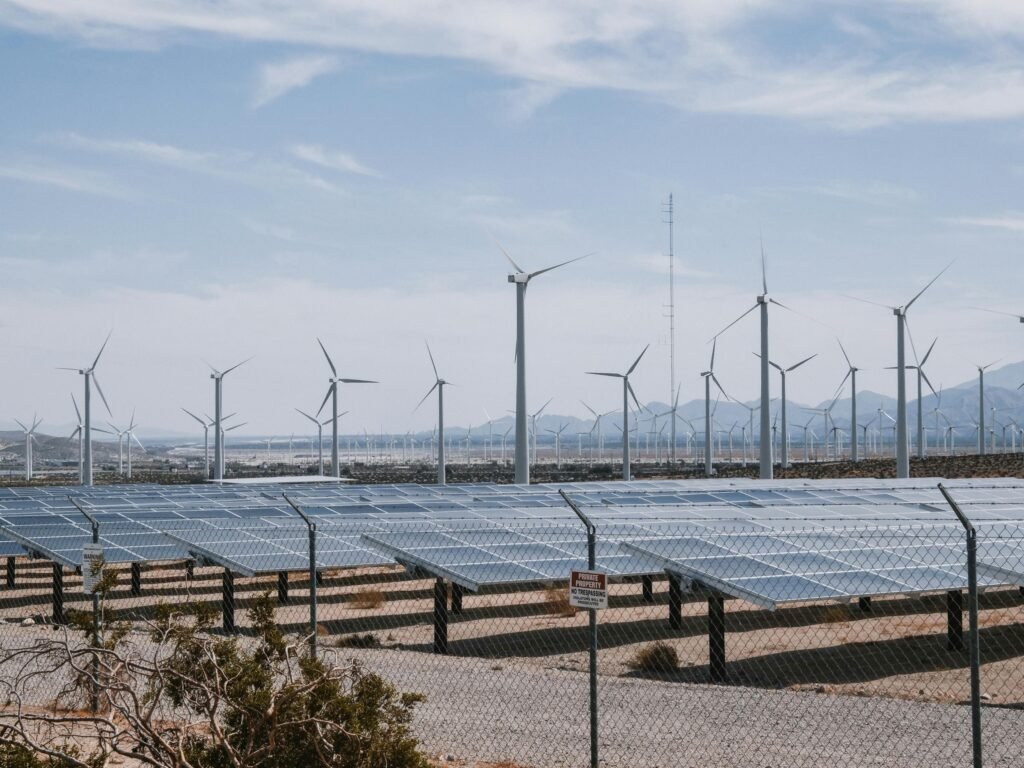

Benefits of Hybrid Renewable Energy Projects
Hybrid renewable energy projects offer several advantages over standalone solar or wind projects:
- Increased Stability and Reliability: By combining complementary resources, hybrid systems reduce the variability and intermittency associated with individual renewable energy sources. This leads to a more stable and reliable power supply, which is crucial for grid stability and meeting energy demands. Hybrid systems can adjust their energy sourcing strategies based on geographical location, selecting the most efficient and abundant local resources, switching between solar and wind as needed.
- Reduced Land Use: Hybrid projects can optimize land use by co-locating wind and solar installations, minimizing the overall land footprint required for renewable energy generation.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Sharing infrastructure such as transmission lines and substations can lead to cost reductions in hybrid projects.
- Higher Capacity Utilization Factor: The utilization or Plant Load Factor (PLF) of an individual wind farm in India today is approximately 35%, while that of an individual solar farm is approximately 17%. However, when these two projects are co-located and hybridized, the effective PLF can go up to 52%, meaning better efficiency for the developer and more efficient utilization for the grid operator.
- Environmental Benefits: Hybrid projects contribute to reduced carbon emissions and a cleaner environment by promoting the use of renewable energy sources.
- Hybrid Power Exploitability Index (HPEI): The HPEI is a novel index that considers resource simultaneity and capacity factor to identify suitable locations for hybrid projects and demonstrate their viability for base-load and peak-load applications.
- Increased Income Opportunities: Access to power supports the development of small businesses and economic activities, creating employment opportunities and improving livelihoods.
Challenges of Hybrid Renewable Energy Projects
While hybrid renewable energy projects offer significant benefits, they also face certain challenges:
- Grid Integration: Integrating hybrid systems with the existing grid infrastructure can be complex, requiring advanced energy management systems and potential grid upgrades. The fluctuating nature of renewable energy outputs can pose challenges for the existing grid infrastructure, which may not always be equipped to handle them effectively.
- Land Acquisition: Obtaining large tracts of land for hybrid projects involves navigating bureaucratic hurdles and regulatory challenges, which often lead to delays and increased project costs.
- Technical Expertise: Designing, installing, and operating hybrid systems requires specialized technical expertise.
- Cost of Energy Storage: Integrating energy storage, such as batteries, can significantly increase the cost of hybrid projects. However, the declining trend in battery prices is expected to make energy storage a more viable option in the future.
- Limited Suitable Locations: The availability of suitable locations with both good wind and solar resources can be a constraint. While areas in Gujarat, Andhra Pradesh, Maharashtra, and Tamil Nadu are favorable, these areas are limited, which could be an obstacle for India’s WSH capacity expansion.
- Policy Shifts in Wind Energy: The wind energy sector in India has faced policy uncertainties and challenges, including changes in auction mechanisms and tariff structures. These challenges have contributed to the emergence of hybrid projects as a more stable and reliable option.
Government Policies and Incentives Supporting Hybrid Renewable Energy Projects in India
The Indian government has recognized the potential of hybrid renewable energy projects and has implemented policies and incentives to support their development:
- National Wind-Solar Hybrid Policy (2018): This policy provides a framework for promoting grid-connected wind-solar hybrid systems, encouraging technological advancements, and ensuring optimal utilization of resources. It also outlines guidelines for integrating wind and solar plants, including provisions for retrofitting existing projects and incorporating battery storage.
- Financial Incentives: Various incentives, such as concessional custom duty exemptions on components required for manufacturing wind electric generators and viability gap funding for offshore wind energy projects, are available for hybrid projects.
- Renewable Purchase Obligations (RPOs): RPOs mandate that a certain percentage of electricity consumption must come from renewable sources, including hybrid projects. This creates a market for renewable energy and encourages its adoption.
Conclusion
With increasing government support, declining costs of renewable energy technologies, and growing awareness of the benefits of hybrid systems, India is poised to become a global leader in this sector.
Ambitious Renewable Energy Targets: India has set a target of achieving 500 GW of renewable energy capacity by 2030, with hybrid projects playing a crucial role in achieving this goal. Relying solely on wind or solar to achieve this target is not an optimal solution, making hybrid projects essential for diversifying the energy mix and ensuring grid stability.
Growing Investor Interest: Hybrid projects are attracting increasing interest from investors, both domestic and international, further driving their growth. As of December 31, 2023, approximately 1.44 GW of hybrid projects have already been commissioned in India.
By embracing hybrid renewable energy projects, India is not only securing a cleaner and more sustainable energy future but also positioning itself as a global leader in the fight against climate change.
www.hexaclimate.com – Your Net-Zero Partner!
Sources:
- https://encr.pw/Oep8R
- https://l1nq.com/DFVrO
- https://l1nq.com/3l9RF
- https://l1nq.com/LeRky
- https://encr.pw/VX10q
- https://l1nq.com/0WGnk
- https://encr.pw/3Cw5R
- https://encr.pw/eWfQG
- https://l1nq.com/BAW2q
- https://l1nq.com/JvQb5
- https://encr.pw/lcdOs
