Wind Energy in India: Harnessing it’s Potential and Future Outlook
India stands as the fourth-largest wind energy producer globally, boasting an installed capacity of approximately 48 GW as of March 2025. Fueled by a robust indigenous wind power industry and progressive government policies, the nation is leveraging its staggering 1163.9 GW wind potential (at 150 meters) to meet ambitious renewable energy targets, including 500 GW of non-fossil energy by 2030, while reducing its carbon footprint. With a manufacturing base capable of producing 18,000 MW annually, India’s wind sector is a cornerstone of its clean energy strategy.

India’s Wind Energy Potential: A Data-Driven Breakdown
India’s wind resources are immense, site-specific, and concentrated primarily in eight windy states. The National Institute of Wind Energy (NIWE), through over 900 wind-monitoring stations, has mapped this potential with wind resource assessments at various heights:
State-wise Distribution:
| S.No. | State | Wind Potential at 120 m (GW) | Wind Potential at 150 m (GW) |
| 1 | Andhra Pradesh | 74.90 | 123.3 |
| 2 | Gujarat | 142.56 | 180.8 |
| 3 | Karnataka | 124.15 | 169.3 |
| 4 | Madhya Pradesh | 15.40 | 55.4 |
| 5 | Maharashtra | 98.21 | 173.9 |
| 6 | Rajasthan | 127.75 | 284.2 |
| 7 | Tamil Nadu | 68.75 | 95.1 |
| 8 | Telangana | 24.83 | 54.7 |
| Total (8 States) | 676.55 GW | 1136.7 GW | |
| 9 | Others | 18.95 | 27.1 |
| Total | 695.50 GW | 1163.9 GW |
*Source: NIWE, latest assessments*
Gujarat and Rajasthan lead with potentials of 180.8 GW and 284.2 GW at 150 meters, respectively, while Tamil Nadu, with over 10 GW installed, remains the frontrunner in operational capacity. Offshore wind adds another dimension, with an estimated 70 GW potential along the coasts of Gujarat and Tamil Nadu, driven by higher wind speeds (40-50% capacity utilization vs. 25-30% onshore). However, no offshore projects are operational as of 2025, despite ambitious targets of 30 GW by 2030.
Current Landscape: Growth and Industry Dynamics
Installed Capacity and Progress
As of March 2025, India’s wind energy capacity stands at approximately 48 GW, up from 45 GW in early 2024, reflecting steady growth driven by private sector investments and technological advancements like turbines up to 5.2 MW. This positions India behind only China, the USA, and Germany in global rankings, with the sector supported by a manufacturing ecosystem producing 18,000 MW annually — 70-80% indigenized.
Recent Developments
The waiver of Inter-State Transmission System (ISTS) charges for projects commissioned by June 2025 has boosted inter-state power sales, while the shift to Tariff-Based Competitive Bidding has driven tariffs down to ₹2.5-3/unit from ₹4-5/unit under the earlier feed-in-tariff system.
Government Policies and Initiatives: A Supportive Framework
The Indian government has implemented a multi-pronged strategy to promote wind energy:
1. Fiscal and Financial Incentives:
- Accelerated Depreciation: Reduces tax liability for developers.
- Concessional Customs Duty: Exemptions on wind generator components.
- Generation-Based Incentives (GBI): Available for projects commissioned before March 31, 2017.
- ISTS Charge Waiver: For inter-state wind power sales until June 2025.
2. Policy Frameworks:
- Wind Renewable Purchase Obligation (RPO): Mandates 43.33% renewable energy procurement by 2030, though only four states—Himachal Pradesh, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, and Tamil Nadu—met the 19% target for 2020-21.
- Tariff-Based Competitive Bidding Guidelines: Standardizes procurement, achieving cost-effective rates.
- National Wind-Solar Hybrid Policy (2018): Encourages hybrid systems for optimized power supply.
- Offshore Wind Energy Policy: Targets coastal potential, though progress lags.
3. Technical Support:
- NIWE’s 900+ monitoring stations and wind potential maps (50m, 80m, 100m, 120m, 150m) guide site selection and project planning.

Opportunities for Investors and Developers
- Offshore Wind Farms: Untapped 70 GW potential offers higher efficiency and larger project scales, with Gujarat and Tamil Nadu as prime zones.
- Repowering Aging Turbines: Over 25 GW of old turbines (<1 MW) can be upgraded to 3-4 MW models, almost doubling output per site.
- Wind-Solar Hybrids: Complementary resources (wind at night, solar by day) enhance reliability, with 50 GW+ potential identified.
- Manufacturing and Supply Chain: With 18,000 MW/year capacity and multiple active companies, India’s wind sector supports local jobs and export potential.
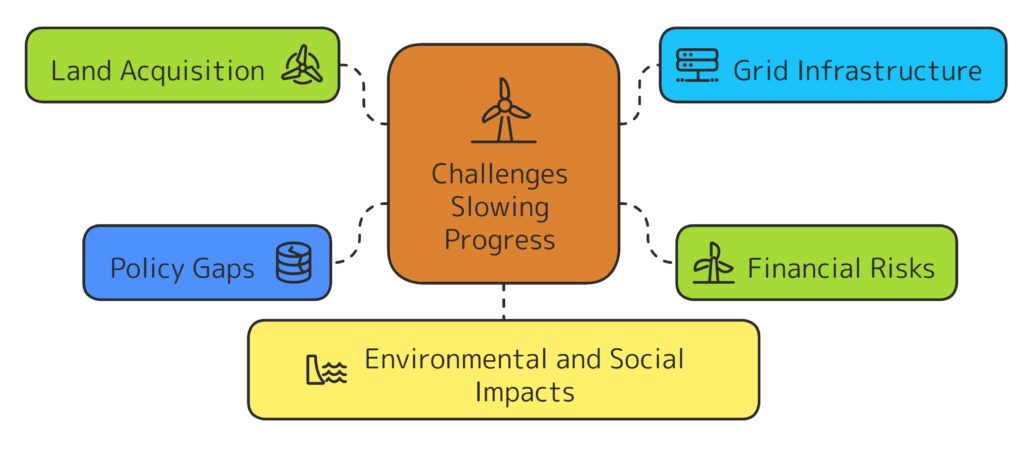
Challenges Slowing Progress
Despite its potential, the wind sector faces significant hurdles:
- Land Acquisition: Projects require 7-8 acres per turbine, leading to delays in permits and clearances.
- Grid Infrastructure: The current transmission network struggles with wind’s intermittent nature, necessitating green energy corridors and smart grids.
- Financial Risks:
- Aggressive bidding has slashed tariffs to ₹2.5-3/unit, reducing profitability.
- Discom defaults strain finances.
- Policy Gaps: No formal framework exists for repowering or recycling old turbines, limiting efficiency gains.
- Environmental and Social Impacts: Ecological concerns and community resistance require careful mitigation.
To unlock its wind potential, India must:
- Strengthen Grid Infrastructure: Invest in smart grids, energy storage, and transmission upgrades.
- Boost R&D: Innovate in offshore technology, turbine efficiency, and hybrid systems.
- Streamline Approvals: Implement single-window clearances for land and permits.
- Skill Development: Train a workforce for offshore, hybrid, and repowering projects.
- Policy Evolution: Finalize repowering and recycling guidelines to maximize existing sites.
Conclusion
India’s wind energy sector, with its 48 GW installed capacity and 1163.9 GW potential, is at a pivotal moment. Backed by a world-class manufacturing base and policies like RPO and ISTS waivers, it can drive the nation toward its 2030 renewable goals. Addressing challenges—grid upgrades, financial sustainability, and land issues—while capitalizing on offshore wind, repowering, and hybrids, will solidify India’s role as a global wind energy leader and advance its net-zero ambitions.
www.hexaclimate.com – Your Net-Zero Partner!
Sources:
- https://l1nq.com/1BZl6
- https://l1nq.com/BConX
- https://l1nq.com/eBMqB
- https://encr.pw/CvdvB
- https://l1nq.com/qmbAQ
